This website uses cookies so that we can offer you the best possible user experience. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognizing you when you return to our website or helping our team understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Project 02
Adult neurogenesis
in animal models of disease
Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, PID2020-113007RB-I00 and PID2023-146572OB-I00.
Further reading
The award of two currently active grants by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (PID2020-113007RB-I00 and PID2023-146572OB-I00 ) will allow us to deepen our knowledge on the regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in distinct model organisms.
Principal Investigator
María Llorens-Martín
Summary
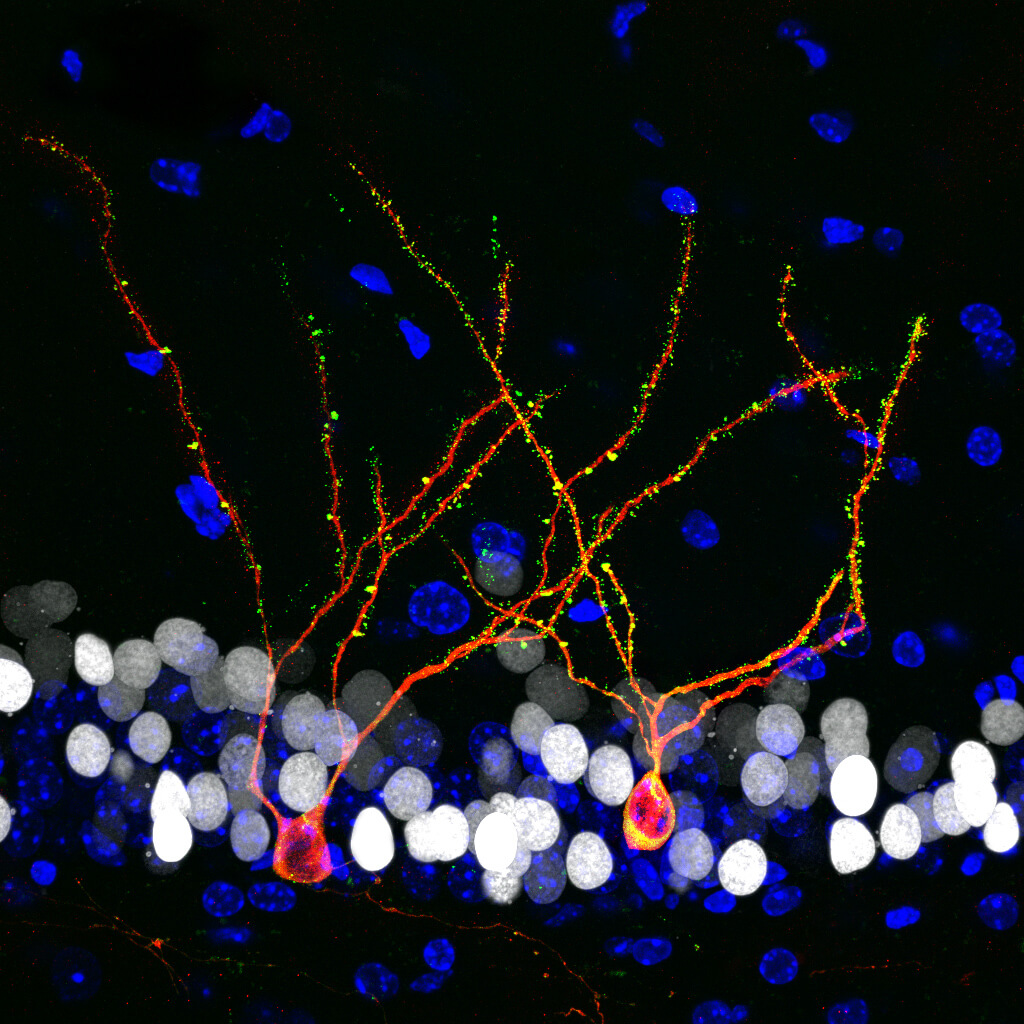
We have developed innovative viral tools to explore the synaptic integration of newborn dentate granule cells from a holistic point of view. Not only we study the establishment and maturation of synaptic contacts made onto these cells, but also the modulation of this process exerted by other elements, such as microglia, astrocytes, interneurons, and vascular elements, which orchestrate the hippocampal trisynaptic circuitry. The use of viral tools, advanced microscopy techniques, single-cell RNA sequencing, and spatial transcriptomics are expected to bring to light the complex remodeling of the hippocampal dentate gyrus neurogenic niche that occurs throughout physiological and pathological aging in mice. We are also assessing the therapeutic potential of novel strategies, either pharmacological or non-pharmacological, to reverse both the cellular and behavioral alterations observed in mouse models throughout aging and under neurodegenerative conditions. Whether or not certain mammalian species are capable of sustaining neurogenesis throughout adult life is still a matter of debate in the field. We are applying the knowledge obtained from human studies to shed some light on these crucial phylogenetic aspects.
Members of the team involved
María Llorens-Martín (Principal Investigator)
Berenice Márquez-Valadez
Carla Rodríguez-Moreno
Elena Moreno-Jiménez
Fabio Cafini (Collaborator)
Julia Terreros-Roncal
Marta Gallardo-Caballero
Miguel Flor-García
-
Participating Institutions
Spanish Research Council (CSIC) (Spain) (Host Institution)
CIBERNED (Spain)
Results Obtained
Publications
a
Azithromycin preserves adult hippocampal neurogenesis and behavior in a mouse model of sepsis.
Rodríguez-Moreno CB, Cañeque-Rufo H, Flor-García M, Terreros-Roncal J, Moreno-Jiménez EP, Pallas-Bazarra N, Bressa C, Larrosa M, Cafini F, Llorens-Martín M. (2024)
Brain Behavior and Immunity
Mar;117:135-148.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.01.005.
Link →
Expand Abstract: The mammalian hippocampus can generate new neurons throughout life. Known as adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN), this process participates in learning, memory, mood regulation, and forgetting. The continuous incorporation of new neurons enhances the plasticity of the hippocampus and contributes to the cognitive reserve in aged individuals. However, the integrity of AHN is targeted by numerous pathological conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases and sustained inflammation. In this regard, the latter causes cognitive decline, mood alterations, and multiple AHN impairments. In fact, the systemic administration of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from E. coli to mice (a model of sepsis) triggers depression-like behavior, impairs pattern separation, and decreases the survival, maturation, and synaptic integration of adult-born hippocampal dentate granule cells.
Here we tested the capacity of the macrolide antibiotic azithromycin to neutralize the deleterious consequences of LPS administration in female C57BL6J mice. This antibiotic exerted potent neuroprotective effects. It reversed the increased immobility time during the Porsolt test, hippocampal secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and AHN impairments. Moreover, azithromycin promoted the synaptic integration of adult-born neurons and functionally remodeled the gut microbiome. Therefore, our data point to azithromycin as a clinically relevant drug with the putative capacity to ameliorate the negative consequences of chronic inflammation by modulating AHN and hippocampal-related behaviors.
b
Prolonged fixation and post-mortem delay impede the study of adult neurogenesis in mice.
Gallardo-Caballero M, Rodríguez-Moreno CB, Álvarez-Méndez L, Terreros-Roncal J, Flor-García M, Moreno-Jiménez EP, Rábano A, Llorens-Martín M. (2023)
Communications Biology
Sep 23;6(1):978.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05367-z.
Link →
Expand Abstract: Adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) gives rise to new neurons throughout life. This phenomenon takes place in more than 120 mammalian species, including humans, yet its occurrence in the latter was questioned after one study proposed the putative absence of neurogenesis markers in the adult human hippocampus. In this regard, we showed that prolonged fixation impedes the visualization of Doublecortin+ immature neurons in this structure, whereas other authors have suggested that a dilated post-mortem delay (PMD) underlies these discrepancies. Nevertheless, the individual and/or additive contribution of fixation and the PMD to the detection (or lack thereof) of other AHN markers has not been studied to date.
To address this pivotal question, we used a tightly controlled experimental design in mice, which allowed the dissection of the relative contribution of the aforementioned factors to the visualization of markers of individual AHN stages. Fixation time emerged as the most prominent factor globally impeding the study of this process in mice. Moreover, the visualization of other particularly sensitive epitopes was further prevented by prolonged PMD. These results are crucial to disambiguate current controversies related to the occurrence of AHN not only in humans but also in other mammalian species.
c
GSK-3β orchestrates the inhibitory innervation of adult-born dentate granule cells in vivo.
Moreno-Jiménez EP, Flor-García M, Hérnandez-Vivanco A, Terreros-Roncal J, Rodríguez-Moreno CB, Toni N, Méndez P, Llorens-Martín M. (2023)
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
Jul 23:80(8): 225.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04874-w.
Link →
Expand Abstract: Adult hippocampal neurogenesis enhances brain plasticity and contributes to the cognitive reserve during aging. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is impaired in neurological disorders, yet the molecular mechanisms regulating the maturation and synaptic integration of new neurons have not been fully elucidated. GABA is a master regulator of adult and developmental neurogenesis. Here we engineered a novel retrovirus encoding the fusion protein Gephyrin:GFP to longitudinally study the formation and maturation of inhibitory synapses during adult hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo. Our data reveal the early assembly of inhibitory postsynaptic densities at 1 week of cell age. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 Beta (GSK-3β) emerges as a key regulator of inhibitory synapse formation and maturation during adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
GSK-3β-overexpressing newborn neurons show an increased number and altered size of Gephyrin+ postsynaptic clusters, enhanced miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents, shorter and distanced axon initial segments, reduced synaptic output at the CA3 and CA2 hippocampal regions, and impaired pattern separation. Moreover, GSK-3β overexpression triggers a depletion of Parvalbumin+ interneuron perineuronal nets. These alterations might be relevant in the context of neurological diseases in which the activity of GSK-3β is dysregulated.
d
GSK-3β S9A overexpression leads murine hippocampal neural precursors to acquire an astroglial phenotype in vivo.
Moreno-Jiménez EP, Flor-García M, Hérnandez-Vivanco A, Terreros-Roncal J, Rodríguez-Moreno CB, Toni N, Méndez P, Llorens-Martín M. (2023)
Developmental Neurobiology
Jul; 81(5):710-723.
doi: 10.1002/dneu.22823.
Link →
Expand Abstract: The addition of new neurons to the existing hippocampal circuitry persists in the adult dentate gyrus (DG). During this process, named adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN), adult hippocampal progenitor cells (AHPs) give rise to newborn dentate granule cells (DGCs). The acquisition of a neuronal lineage by AHPs is tightly regulated by numerous signaling molecules and transcription factors. In this regard, glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) is a master regulator of the maturation of AHPs in vitro. Here we analyzed the cell-autonomous effects of overexpressing a constitutively active form of GSK-3β (GSK-3β S9A) in AHPs in vivo. To this end, we stereotaxically injected a GSK-3β S9A-encoding retrovirus (GSK-3β-V5) into the DG of young adult C57BL6/J Ola
Hsd female mice and studied the cell lineage acquisition, migratory and marker expression patterns, and the morphological maturation of the infected cells over time. Strikingly, GSK-3β S9A-transduced cells expressed glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and NG2, thereby acquiring an immature astroglial phenotype, which differed markedly from the neuronal phenotype observed in cells transduced with a control retrovirus that encoded GFP. Accordingly, the morphology and migration patterns of cells transduced by the two retroviruses are remarkably divergent. These observations support the role of GSK-3β as a cornerstone that regulates the balance between new astocytes/neurons generated in the adult murine DG.
Invited talks and conferences
María Llorens-Martín
Eurogenesis, Bordeaux (France), 12 June 2019.
María Llorens-Martín
AGE2021 (Madison, USA), 21 July 2021.
María Llorens-Martín
IBRO2019 (Tsukuba, Japan), 21 July 2021.
Press
Ciberned
Miguel Flor-García. CIBERNED Young Investigator National Award. 19 Oct 2020.
Link →
CSIC
Press release: “Logran “reconectar” un grupo de neuronas dañadas por una enfermedad neurodegenerativa”. 28 May 2019.
Link →
Cadena Ser
“Logran 'reconectar' neuronas dañadas”. 28 May 2019.
Link →
Diario Salud
“Logran “reconectar” un grupo de neuronas dañadas por una enfermedad neurodegenerativa”. 6th June 2019.
Link →
Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CBMSO) Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (Campus de Cantoblanco)
C/ Nicolás Cabrera 1 - 28049 Madrid (Spain)
María Llorens-Martín (PI)
m.llorens@csic.es
+34 911964632